- Knowing when the U.S. economy is heading for recession is paramount to successful investment decisions.
- Our weekly Business Cycle Index would have provided early reliable warnings for the past seven recessions and signaled the Covid 2020 recession one week late.
- The BCIg has signaled a recession warning mid March 2023, but BCIg recovered and is no longer signalling a recession.
- However the BCIw, also on recovery path, continues to signal a recession which now is estimated to begin in 9 to 22 weeks.
- It is too early to say if a recession has been averted, more likely is it is delayed towards the end the end of 2023 or to begin 2024.
The iM Business Cycle Index (BCI) was designed for a timely signal before the beginning of a recession and is fully described in the three articles all found here. In summary, the iM BCI combines the following seven series of economic data: the 10-year treasury yield, 3-month treasury bill yield, S&P500, Continues Claims Seasonally Adjusted, All Employees – Total Private Industries, New houses for sale, and New houses sold.
The BCI on its own does not provide recession signals, but after further manipulation of the series two indicators are extracted that reliable signal looming recessions:
- The six-month smoothed annualized growth rate of an economic series series is a well-established method to extract an indicator from the series. We use this method to obtain BCIg (growth). Here BCIg is the calculated growth rate with 6.0 added to it, which generates, on past performance, an average 11-week leading recession signal when BCIg falls below zero.
- We also found that the BCI retreats in a well-defined manner from its cyclical peak prior to recessions. This allowed the extraction of the alternative indicator BCIp (peak), and its variant BCIw (weeeks). Past performance shows that on average 20 weeks prior to a recession the BCIp value crossed 25 to the downside.
The two indicators BCIg and BCIp could be used as a sell signal for ETFs that track the stock markets, like SPY, IWV, VTI, etc. (see our article) or stocks in general.
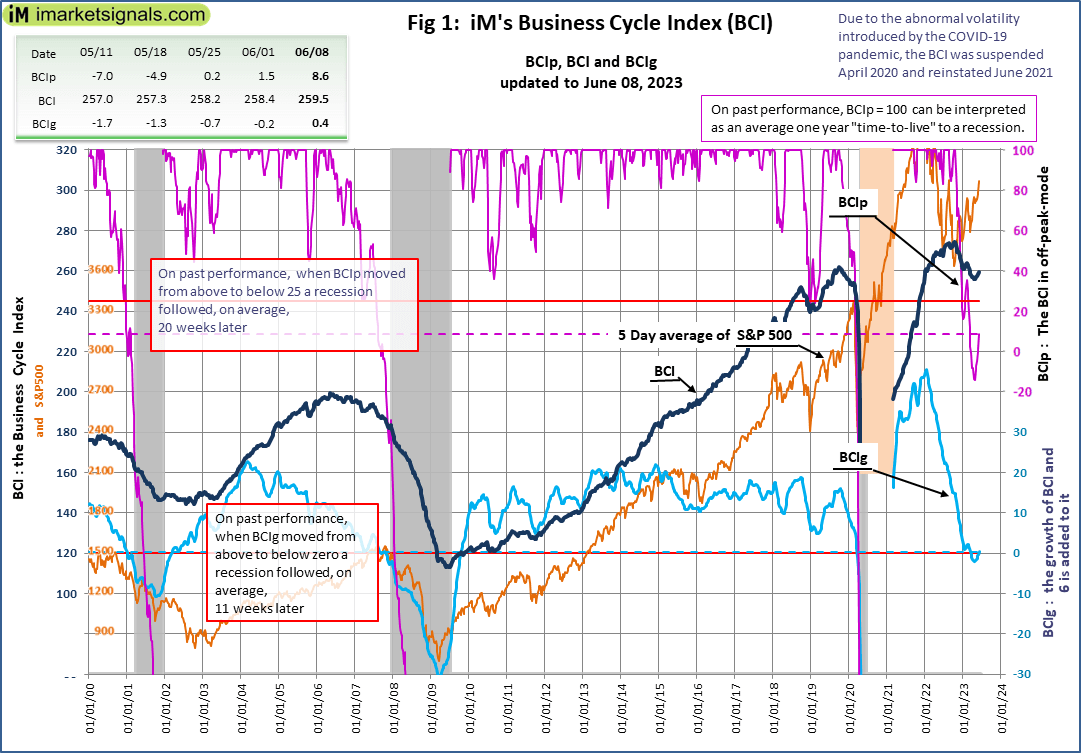
Figure 1 plots BCIp, BCI, BCIg and the S&P 500 together with the thresholds (red lines) that need to be crossed to be able to call a recession. Here we note that BCIp now at 8.6 remains below 25 threshold but trending upwards. Historic data of the past recession shows that at this value the economy never recovered to avoid a recession.
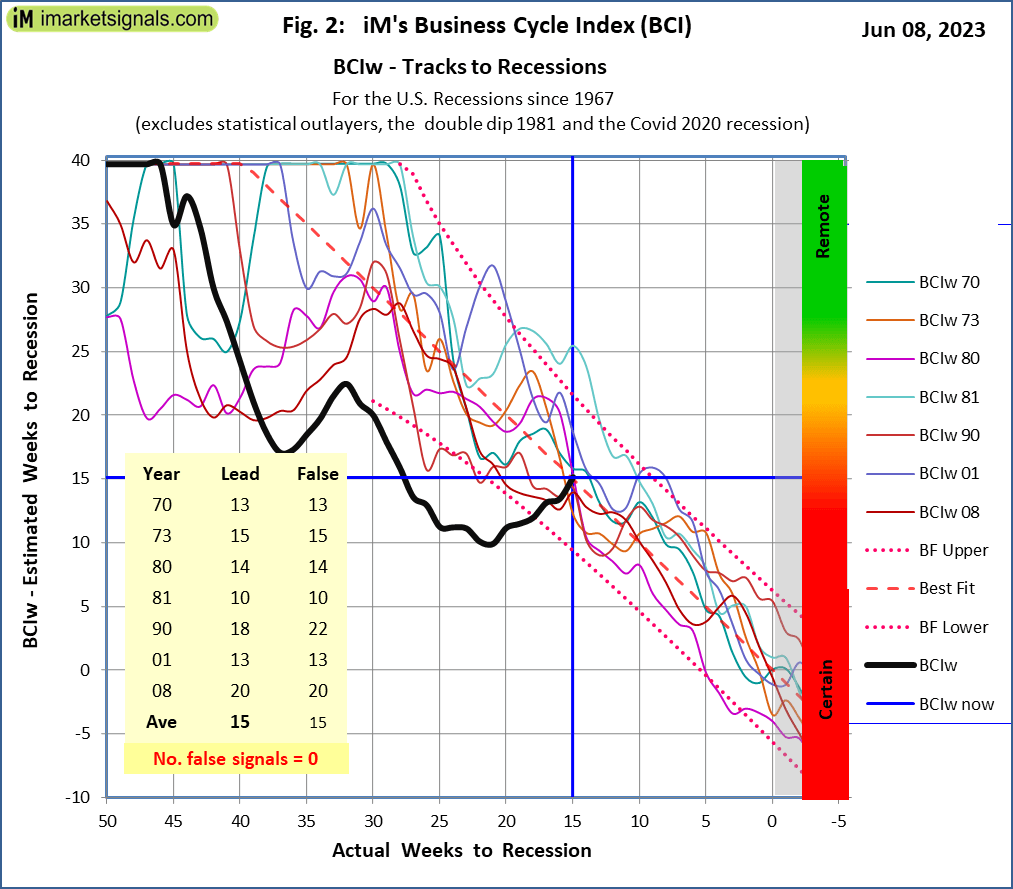
In our 2014 article iM’s BCIw: A Weeks to Recession Indicator on past performance we show how the BCIp (deviation from previous peak of BCI) indicator can be transformed to a BCIw (weeks to next recession) derived from the previous BCIp tracks to the NBER defined recession. The below Figure 2 plots the BCIw tracks to the past recession together with the current value of BCIw with its endpoint on the best fit average value of the past recessions. From this graph we identify that the BCI signals the next recession to begin at an estimated 9 to 22 weeks from now, which is later then what was previous estimated in our update of May 5, 2023.
Has the US economy averted a recession?
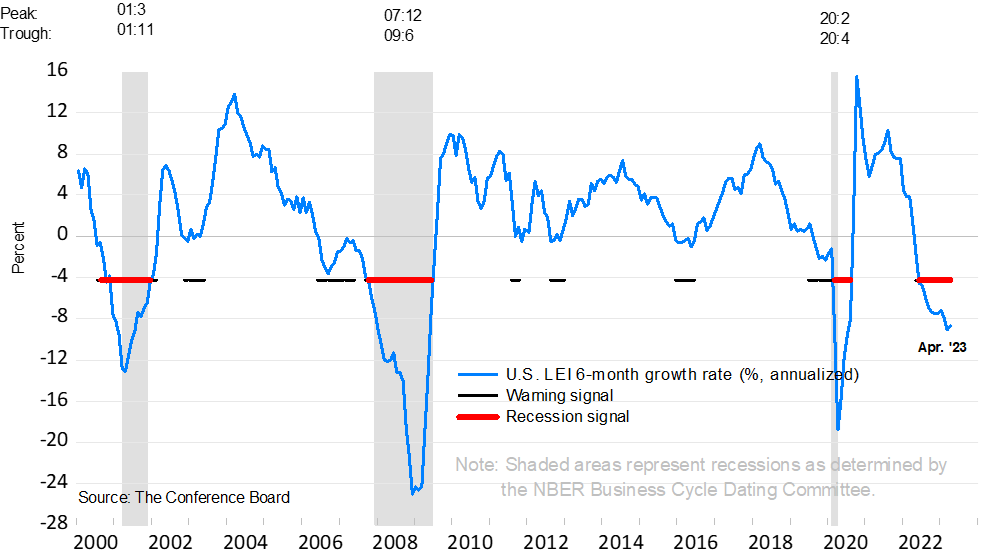
It is too early to answer this question. It is not only the BCI that warns of a coming recession. The Conference Board interpret their US Leading Index (LEI) as signalling a recession:
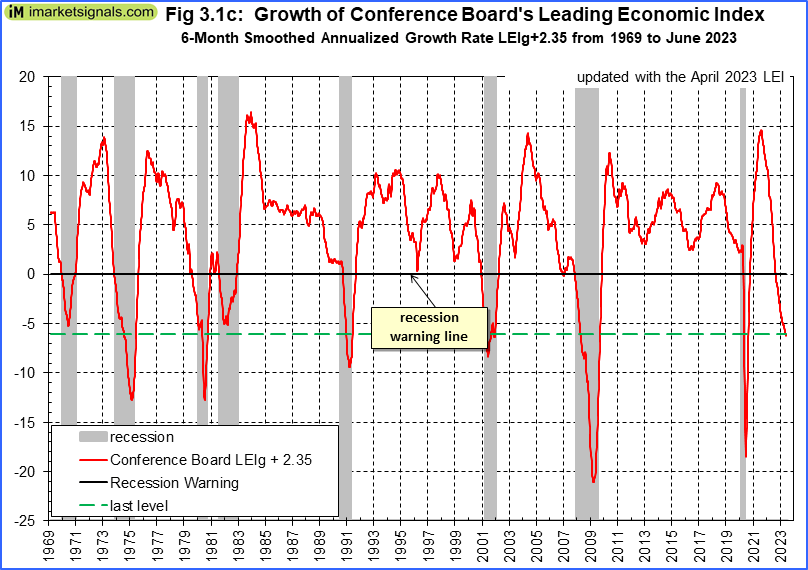
At iMarketSignals we prefer to analyze the 6 month smoothed annualized growth rate of the LEI which is well into recession territory.
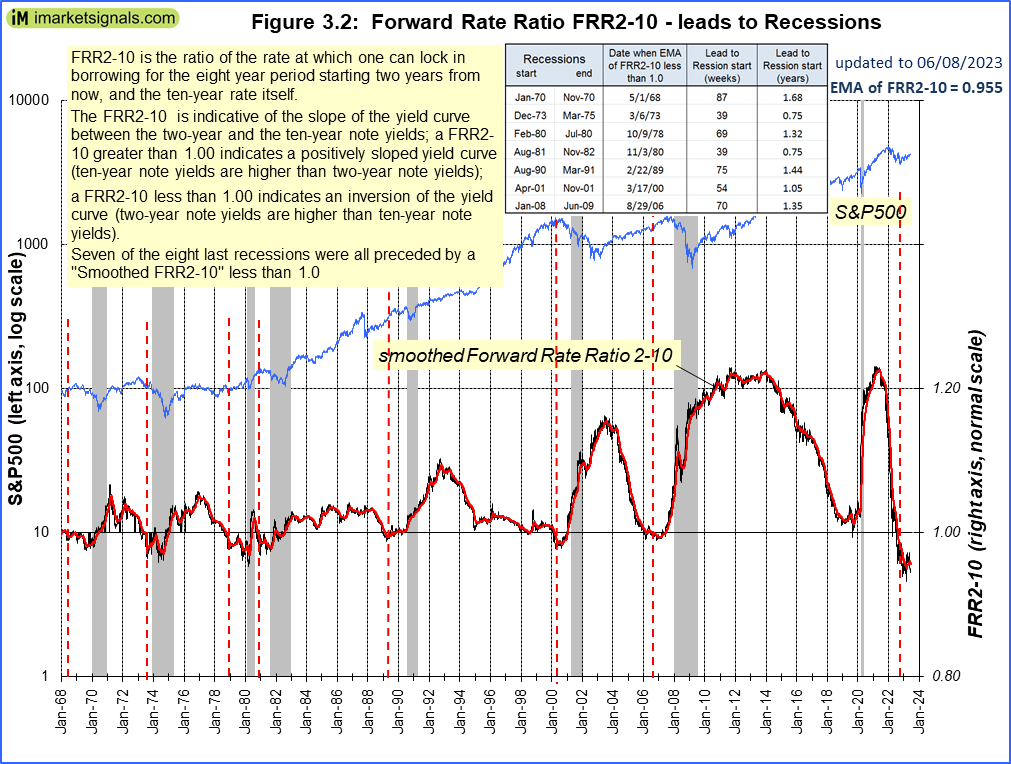
Another of our indicators is the Forward Rate Ratio (FRR2-10) which is indicates the slope of the yield curve between the two and ten-year note yields.
In the past it signals a recession with an average lead time of 1.2 years after inversion. The FFR2-10 is inverted since August 2022.
From the indicators above, and their historic data, a recession remains highly likely probably to begin by the end of 2023 or the beginning of 2024, and it is too early to ignore the recession warnings.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.